인프런의 스프링 입문 - 코드로 배우는 스프링 부트, 웹 MVC, DB 접근 기술를 정리한 글이다.
🏃🏻♀️ 정적 컨텐츠
스프링부트에는 정적인 화면을 보여주는 정적 컨텐츠 기능이 있다.
다음과 같이 src/resources/static 폴더에 hello-static.html을 생성했다.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<title>static content</title>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8" />
</head>
<body>
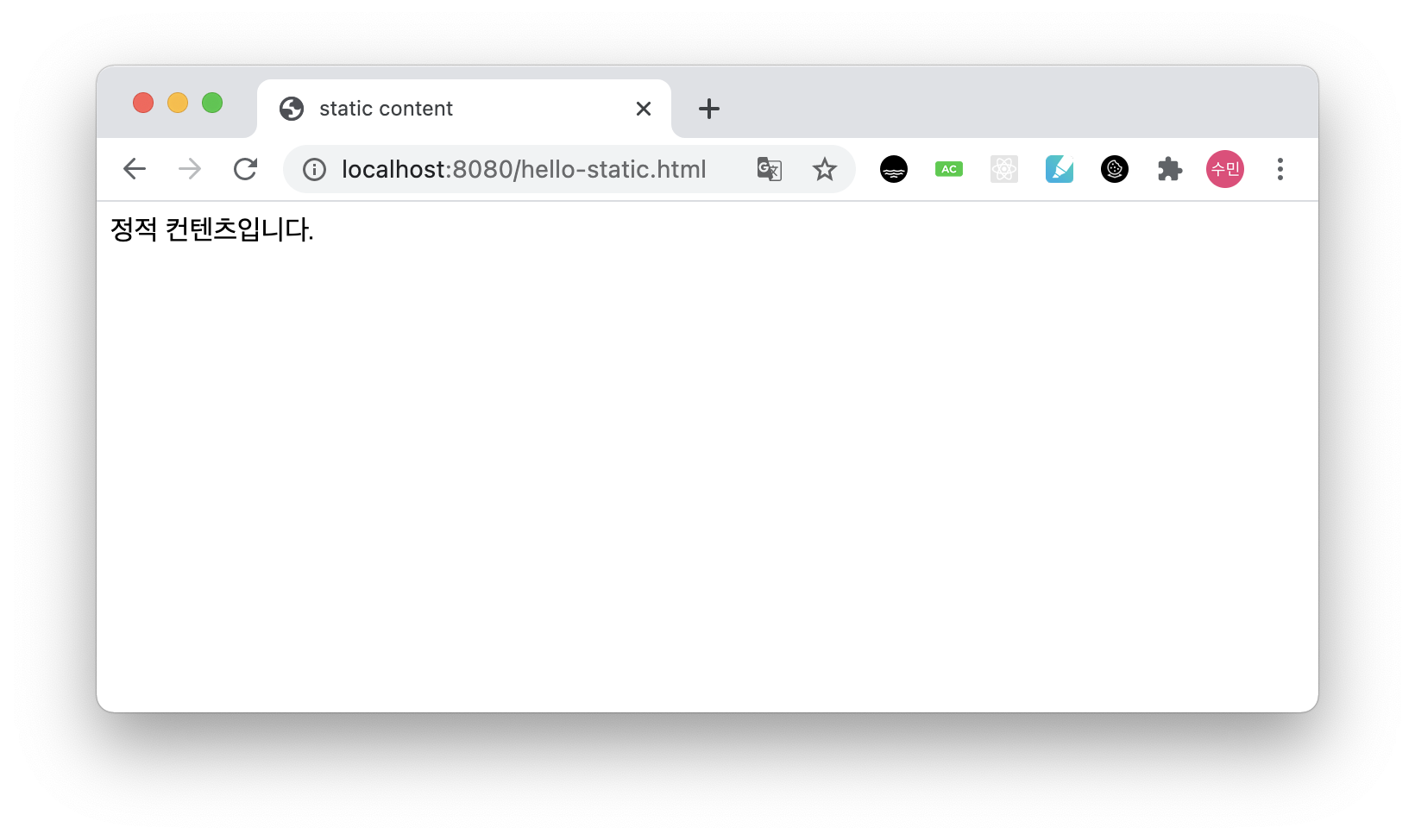
정적 컨텐츠입니다.
</body>
</html>
localhost:8080/hello-static.html을 띄워보면 다음과 같이 나타난다.
정적 콘텐츠 동작
정적 콘텐츠는 다음과 같이 동작한다.
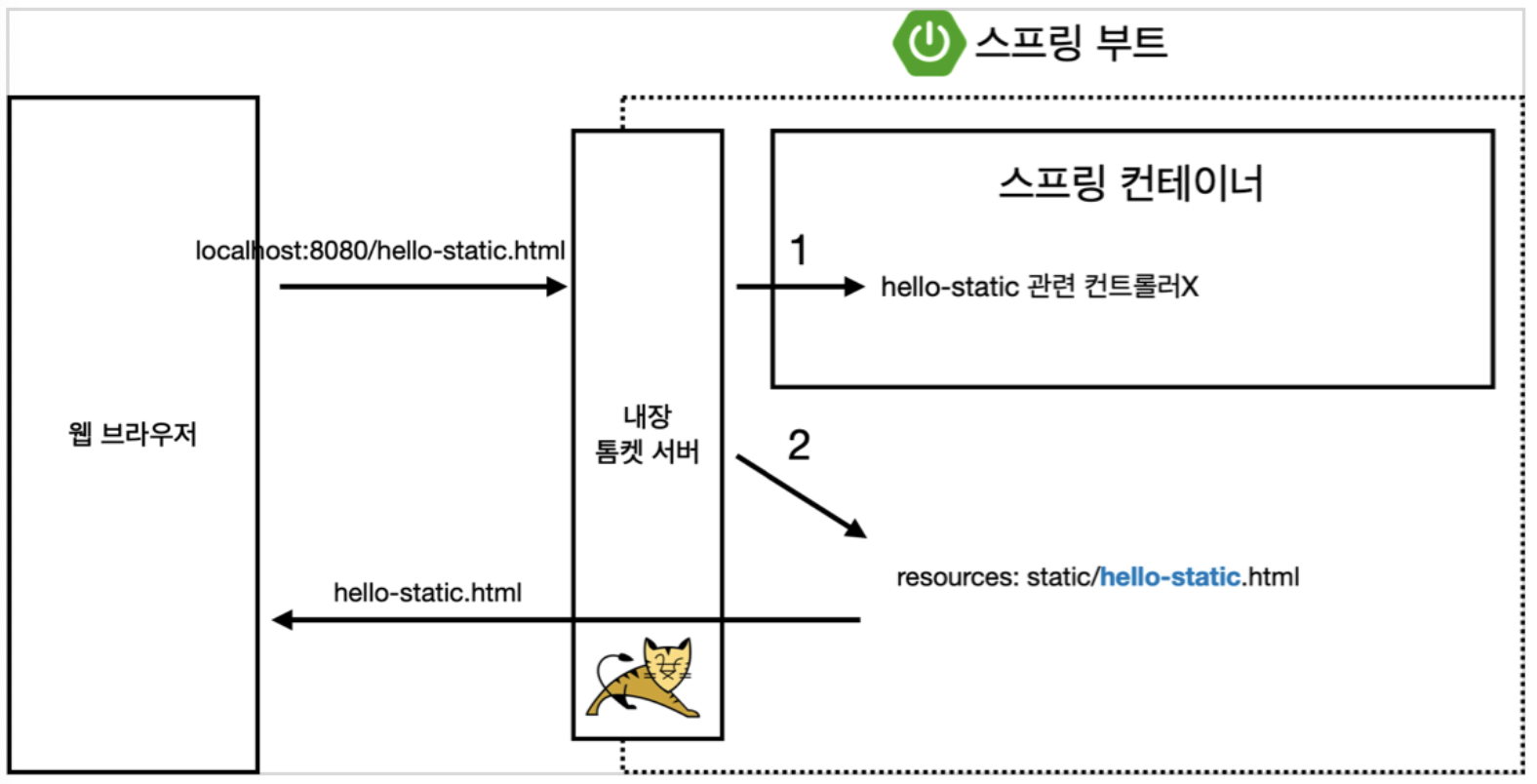
웹 브라우저에서 localhost:8080/hello-static.html로 요청을 보낸다.
그러면 내장된 톰캣 서버가 처리를 해주는데,
1. 먼저 hello-static 관련된 컨트롤러 (src/main/java/hello/hellospring/controller 폴더)를 확인하고, 있다면 해당 컨트롤러로 처리를 해준다.
2. 없다면 resources:static 폴더를 확인해 hello-static과 관련된 정적 파일을 확인하고, 이를 사용자에게 보여준다.
🏃🏻♀️ MVC와 템플릿 엔진
MVC : Model, View, Controller 디자인 패턴
최근에는 Controller와 View로 쪼개는건 기본이다. 각 기능을 쪼개주는 MVC 패턴을 사용한다.

src/main/..../controller 폴더에 앞서 생성해둔 HelloController로 가서 helloMvc를 입력한다.
@Controller
public class HelloController {
// localhost:8080/hello 하면 아래와 매칭이 된다.
@GetMapping("hello") // GET, POST 할 때 그 GET
public String hello(Model model) {
model.addAttribute("data", "hello!"); // hello.html로 넘어갈 데이터
return "hello"; // resources/templates/hello.html로 연결하라는 뜻이다.
}
@GetMapping("hello-mvc")
// name이라는 파라미터를 받을 것이다.
public String helloMvc(@RequestParam("name") String name, Model model) {
model.addAttribute("name", name); // 입력받은 name 파라미터를 hello-template로 넘겨주겠다.
return "hello-template"; // resources/templates/hello-template.html로 연결
}
}helloMvc는 RequestParam으로 name을 받아온다. 즉, 클라이언트로부터 name이라는 파라미터를 입력 받아, model.addAttribute를 사용해 hello-template 파일로 해당 데이터를 넘겨줄 것이다.
resources/templates 폴더에 hello-template.html 파일을 생성한다.
<html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<body>
<p th:text="'hello ' + ${name}">hello! empty</p> <!-- hello! empty는 서버에서 데이터를 주면, hello ${name}으로 내용물이 바뀌게 된다. -->
</body>
</html>p 태그를 보면, 받아온 데이터를 사용해 화면에 "hello ${name}"을 띄워줄 것이다.
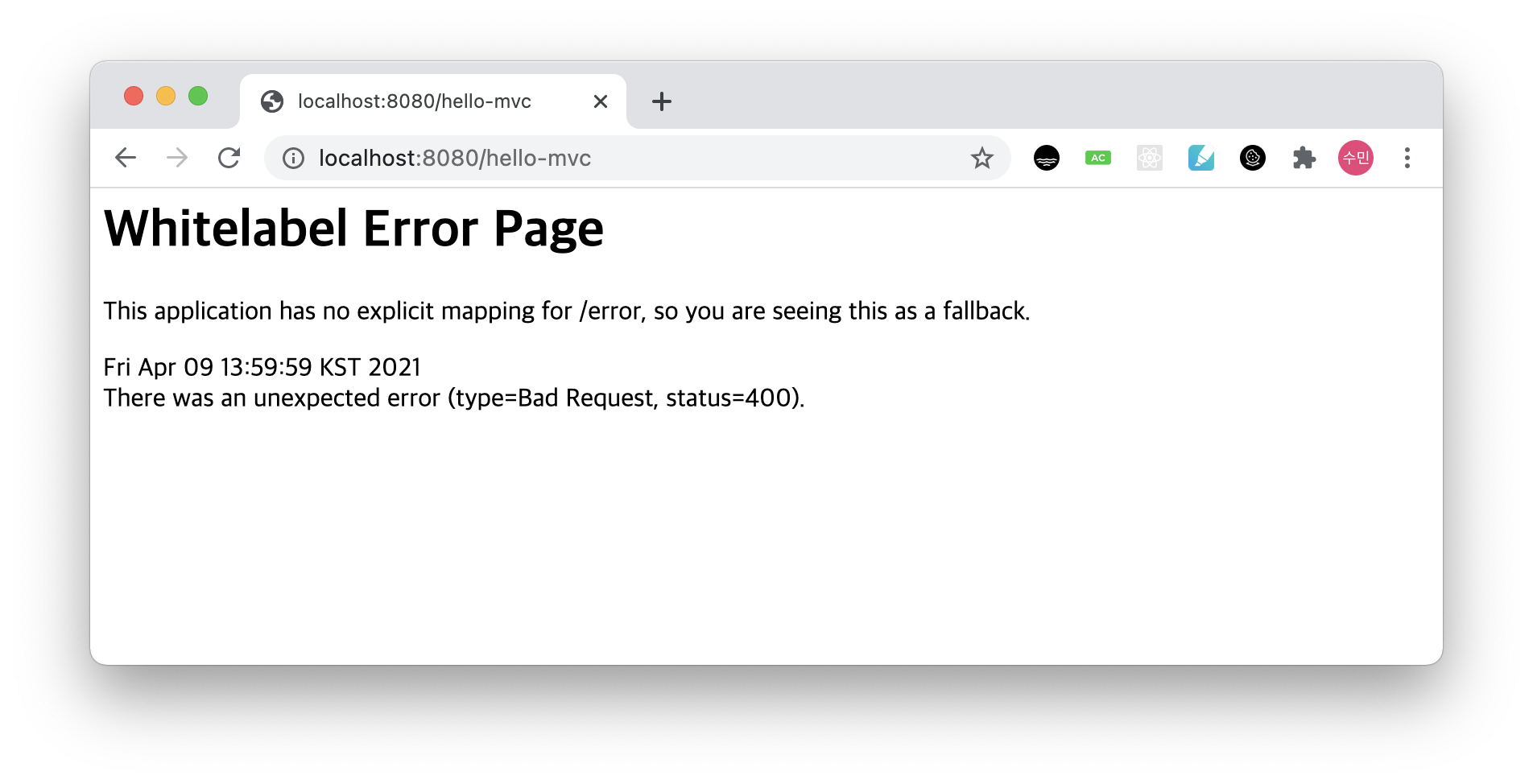
웹 페이지로 localhost:8080/hello-mvc를 띄우면, 다음과 같이 에러 페이지가 나오는데 그 이유는 파라미터로 name값을 넘겨주지 않았기 때문이다.
localhost:8080/hello-mvc?name=spring을 띄우면, name 파라미터를 값(spring)으로 넘겨줬기 때문에 다음과 같이 화면이 정상적으로 나온다.

MVC, 템플릿 엔진 동작
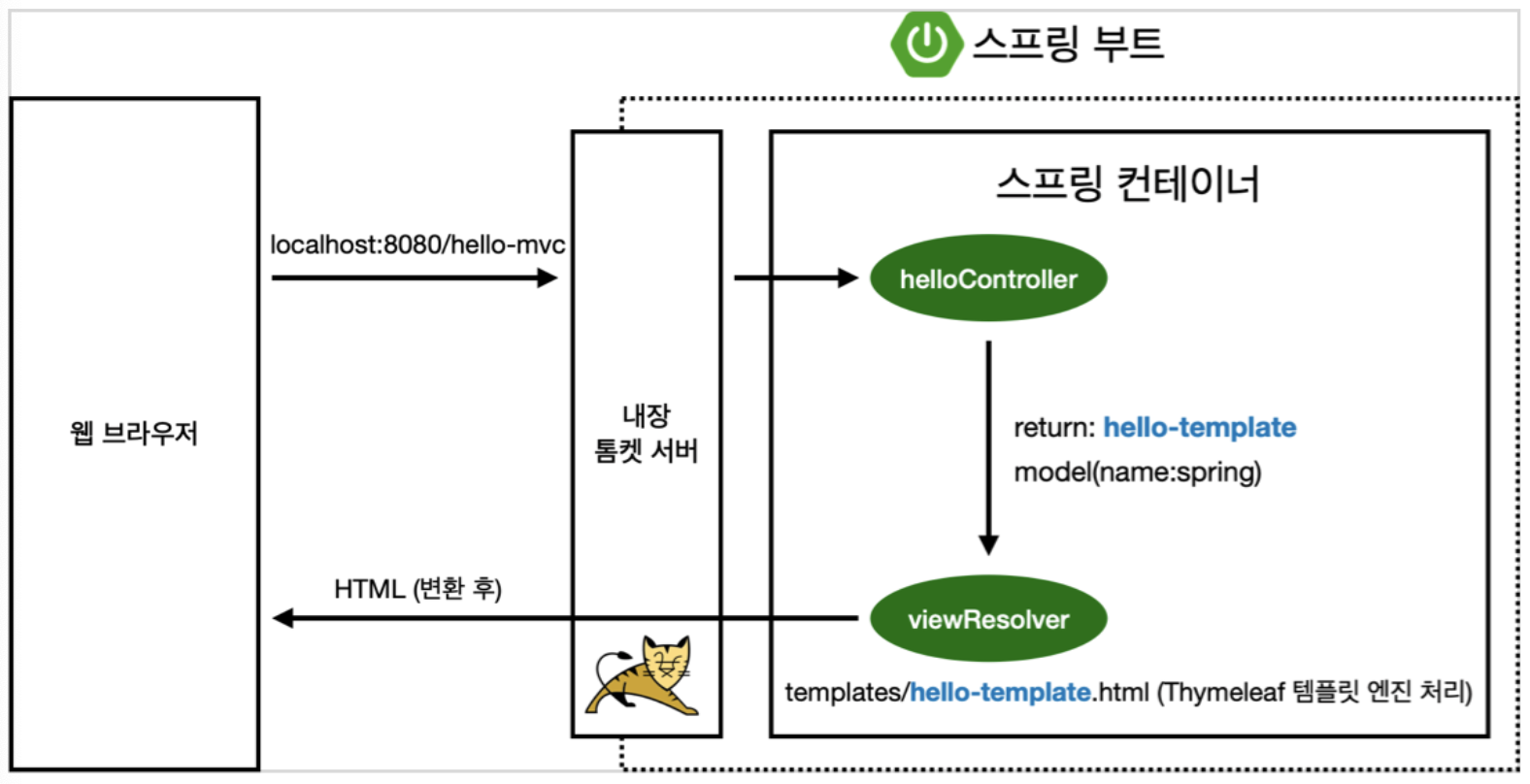
1. 웹 브라우저가 localhost:8080/hello-mvc로 요청을 하면, 내장된 톰캣 서버는 연결된 컨트롤러를 확인한다.
2. 연결된 컨트롤러인 helloController가 데이터를 hello-template으로 전달한다.
3. Thymeleaf 템플릿 엔진이 hello-template 파일을 처리해서 변환된 HTML을 웹 브라우저에 띄워준다.
🏃🏻♀️ API
1. String 반환
HelloController 파일에 helloString을 추가한다. (API 방식 사용)
package hello.hellospring.controller;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.ui.Model;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
@Controller
public class HelloController {
// localhost:8080/hello 하면 아래와 매칭이 된다.
@GetMapping("hello") // GET, POST 할 때 그 GET
public String hello(Model model) {
model.addAttribute("data", "hello!"); // hello.html로 넘어갈 데이터
return "hello"; // resources/templates/hello.html로 연결하라는 뜻이다.
}
// MVC
@GetMapping("hello-mvc")
// name이라는 파라미터를 받을 것이다.
public String helloMvc(@RequestParam("name") String name, Model model) {
model.addAttribute("name", name); // 입력받은 name 파라미터를 hello-template로 넘겨주겠다.
return "hello-template"; // resources/templates/hello-template.html로 연결
}
// API 방식 (return String)
@GetMapping("hello-string")
@ResponseBody // Http 통신 프로토콜에서 Body부에 아래 Return 값을 직접 넣어주겠다.
public String helloString(@RequestParam("name") String name) {
return "hello " + name; // "hello spring"
}
}그리고 실행 후, localhost:8080/hello-string?name=spring!!을 띄우면 다음과 같이 나타난다.
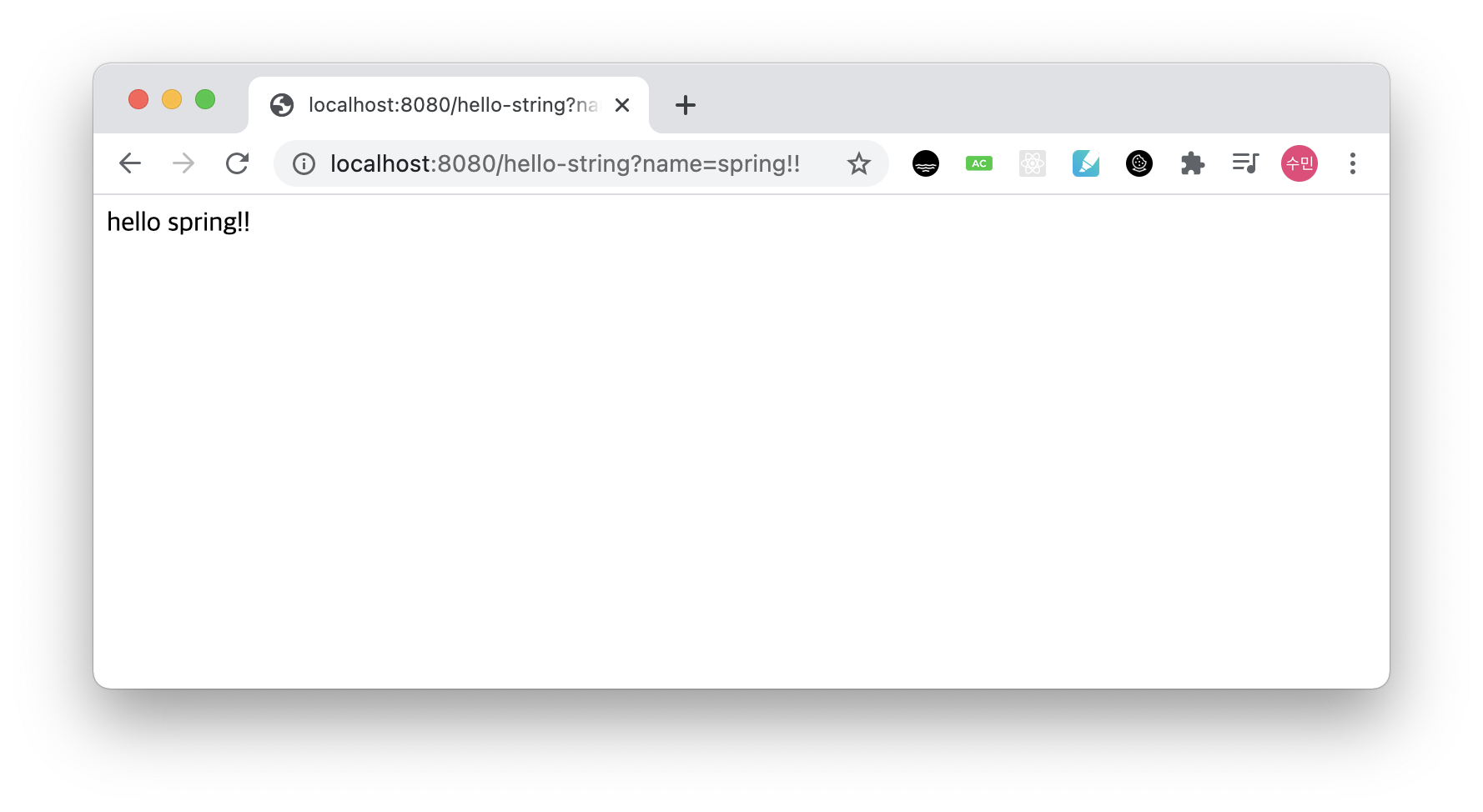
페이지 소스 보기를 하면 다음과 같이 나타나는데, String 값을 반환하기 때문이다.

@ResponseBody를 사용하면 뷰 리졸버(viewResolver)를 사용하지 않는다!
대신 HTTP의 BODY에 문자 내용을 직접! 반환하게 된다. (HTML의 BODY 태그 아님!)
2. 객체 반환
HelloController에 helloApi를 추가한다.
package hello.hellospring.controller;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.ui.Model;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
@Controller
public class HelloController {
// localhost:8080/hello 하면 아래와 매칭이 된다.
@GetMapping("hello") // GET, POST 할 때 그 GET
public String hello(Model model) {
model.addAttribute("data", "hello!"); // hello.html로 넘어갈 데이터
return "hello"; // resources/templates/hello.html로 연결하라는 뜻이다.
}
// MVC
@GetMapping("hello-mvc")
// name이라는 파라미터를 받을 것이다.
public String helloMvc(@RequestParam("name") String name, Model model) {
model.addAttribute("name", name); // 입력받은 name 파라미터를 hello-template로 넘겨주겠다.
return "hello-template"; // resources/templates/hello-template.html로 연결
}
// API 방식 (return String)
@GetMapping("hello-string")
@ResponseBody // Http 통신 프로토콜에서 Body부에 아래 Return 값을 직접 넣어주겠다.
public String helloString(@RequestParam("name") String name) {
return "hello " + name; // "hello spring"
}
// API 방식 (return JSON)
@GetMapping("hello-api")
@ResponseBody
public Hello helloApi(@RequestParam("name") String name) {
Hello hello = new Hello();
hello.setName(name);
return hello; // 객체를 넘긴다!
}
static class Hello { // 객체 생성
private String name;
// getter, setter 생성
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
}
Hello 라는 객체를 생성해주고, 해당 객체를 return한다.
localhost:8080/hello-api?name=spring!!을 띄우면 다음과 같이 JSON 형식이 나타난다.
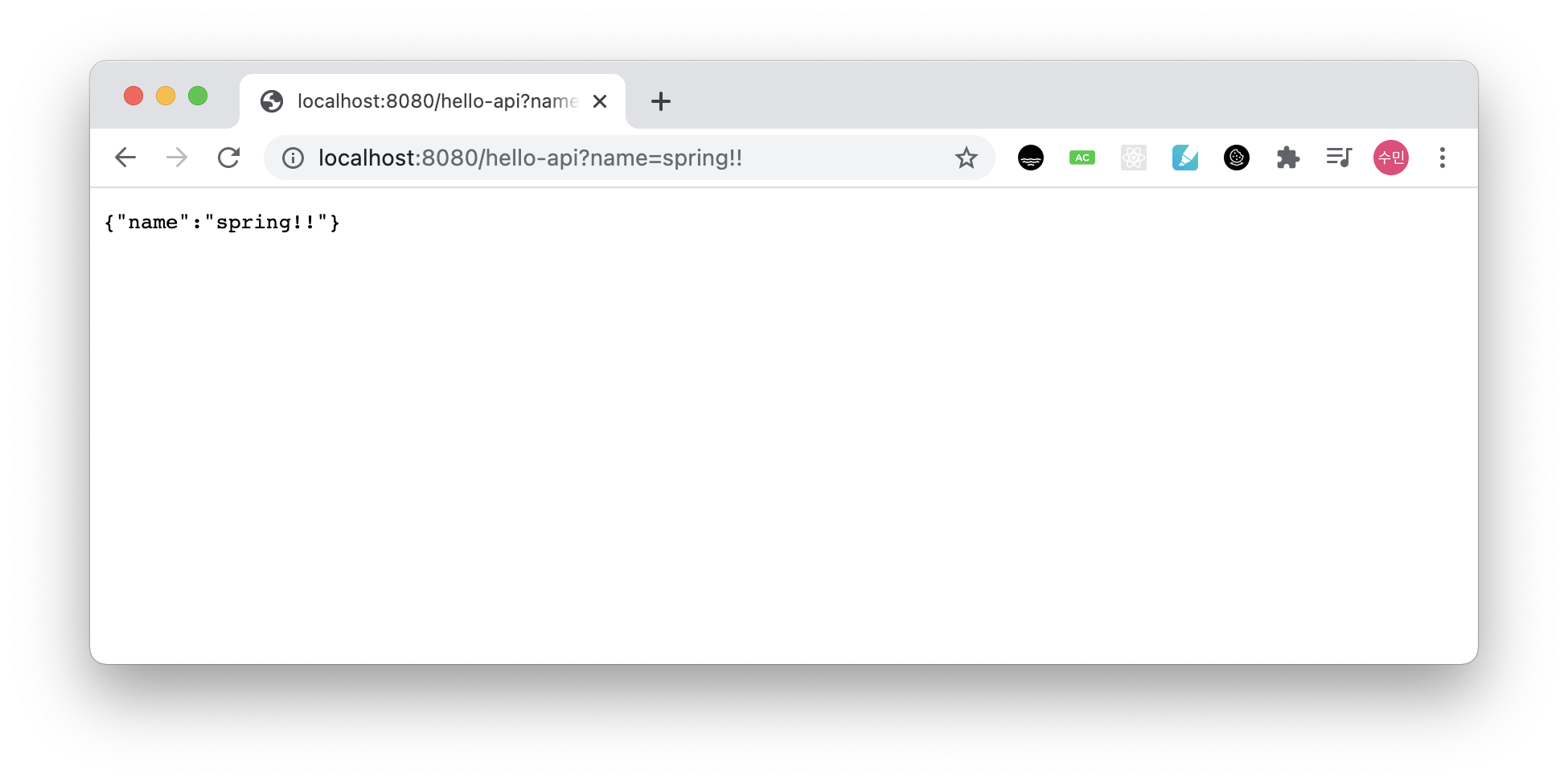
@ResponseBody를 사용하고, 객체를 반환하면 객체가 JSON으로 변환되는 것이다.
@ResponseBody 사용 원리
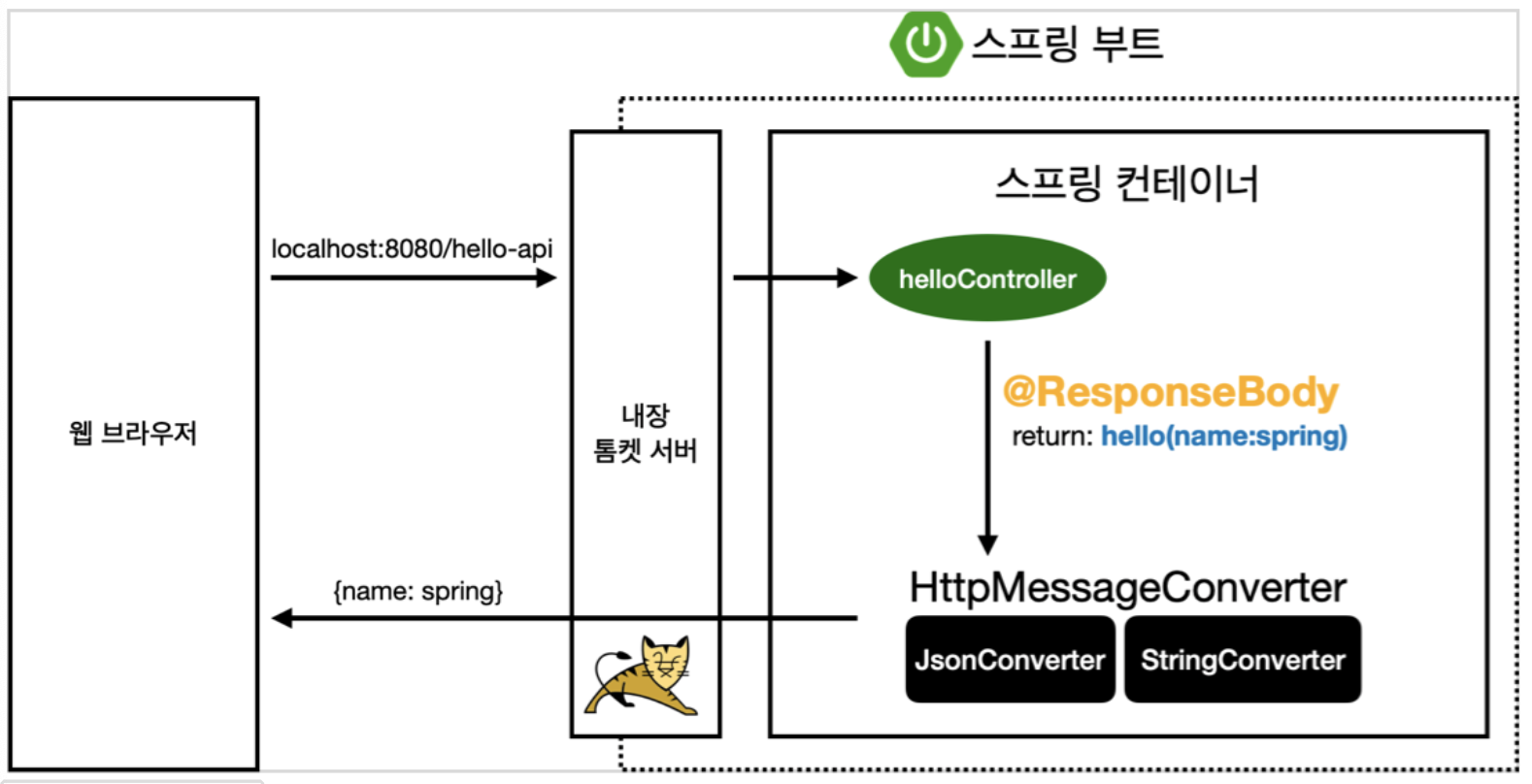
1. localhost:8080/hello-api로 요청이 들어오면, 내장된 톰캣 서버가 이를 스프링 컨테이너로 보낸다.
2. 관련 컨트롤러를 찾는데, 이 때 @ResponseBody가 있다면! viewResolver 대신에 HttpMessageConverter가 동작한다!
3. 기본 문자일 경우, StringHttpMessageConverter가 처리를 하고,
4. 기본 객체일 경우, MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter가 처리를 해준다.
5. byte 처리 등등 기타 여러 HttpMessageConverter가 기본으로 등록되어 있다.
-> 각 타입마다 해당 MessageConverter가 처리를 해준다.
'개발새발 개발하기' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Spring] 스프링 빈과 의존관계 (0) | 2021.04.14 |
|---|---|
| [Spring] 회원 관리 예제 (백엔드 개발) (0) | 2021.04.13 |
| [Spring] Spring 개발환경 구축하기 (0) | 2021.04.08 |
| [Swagger] Node.js에 Swagger 적용하기 (2) - OpenApI (0) | 2020.12.13 |
| [Swagger] Node.js에 Swagger 적용하기 (1) (0) | 2020.12.06 |



